Neural Network Algorithm Example
DeepStack, one of many recent computers to face off against human beings, defeated 11 professional poker players in heads-up no-limit hold'em, according to a study published in Science this month.
Using neural networks has become standard in many areas of the industry. However, the challenge was to design a learning algorithm for the game of Poker, which is a very complex multi-player game with hidden information. The prediction 1 is served as one of input features for second neural network. Other features including odd or even, prime property and equality are standardized by the StandardScaler function. Train the second neural network using backpropagation algorithm. The second neural network has 200x100x50 neurons 3 hidden layers. Mazur used neural network for design a computer bot that plays poker. This time another type of poker game is concerned. Player will receive two cards and five cards will be on the table, at first three cards.
Of the 11 players, DeepStack defeated 10 of them in December 2016 by statistically significant margins after the study authors had the computer undergo deep learning training to teach the bot to develop poker intuition for any situation.
The computer looked up two copies of the same network in its neural network, namely for the first three shared cards and then again for the final two, trained on 10,000 randomly drawn poker games, reported Ars Technica.
Neural networks approach the problem in a different way. The idea is to take a large number of handwritten digits, known as training examples, and then develop a system which can learn from those training examples. In other words, the neural network uses the examples to automatically infer rules for recognizing handwritten digits. Seminole casino immokalee events november.
The researchers recruited 33 players through the International Federation of Poker.
Only 11 players finished 3,000 matches over the course of a four-week period and DeepStack's neural networks were what allowed it to essentially 'learn' and model higher-level concepts while it ran on a gaming laptop (NVIDIA GTX 1080). DeepStack was developed by researchers at the University of Alberta and a number of Czech universities.
DeepStack works through situations as humans would, learning pieces of the game as it goes and create a strategy to defeat the humans.
'In some sense this is probably a lot closer to what humans do,' said Michael Bowling, professor of machine learning and the study author, to Scientific American. 'Humans certainly don't, before they sit down and play, precompute how they're going to play in every situation. And at the same time, humans can't reason through all the ways the poker game would play out all the way to the end.'
DeepStack isn't the only artificial intelligence out there. Carnegie Mellon's Libratus recently beat four professional players with a more elite status on a supercomputer. Its technology is similar to that of DeepStack in the later stages of computing but it does not use the same neural networks, according to Scientific American. DeepStack also won by larger margins.
Past attempts with Claudico didn't pan out, but Google DeepMind's Alpha Go beat pros at the game, go. Even more notably, 20 years ago, Deep Blue beat World Chess Champion Garry Kasparov at his own game.
This finding reveals a lot about artificial intelligence's ability to master imperfect information games beyond abstraction (or computing how to play in every situation before the game begins).
Lead image courtesy of Thigala shri/Flickr
Tags
Poker PlayersAI
Editor's note: One of the central technologies of artificial intelligence is neural networks. In this interview, Tam Nguyen, a professor of computer science at the University of Dayton, explains how neural networks, programs in which a series of algorithms try to simulate the human brain work.
What are some examples of neural networks that are familiar to most people?
There are many applications of neural networks. One common example is your smartphone camera's ability to recognize faces.
Driverless cars are equipped with multiple cameras which try to recognize other vehicles, traffic signs and pedestrians by using neural networks, and turn or adjust their speed accordingly.
Neural networks are also behind the text suggestions you see while writing texts or emails, and even in the translations tools available online.
Does the network need to have prior knowledge of something to be able to classify or recognize it?
Yes, that's why there is a need to use big data in training neural networks. They work because they are trained on vast amounts of data to then recognize, classify and predict things.
In the driverless cars example, it would need to look at millions of images and video of all the things on the street and be told what each of those things is. When you click on the images of crosswalks to prove that you're not a robot while browsing the internet, it can also be used to help train a neural network. Only after seeing millions of crosswalks, from all different angles and lighting conditions, would a self-driving car be able to recognize them when it's driving around in real life.
More complicated neural networks are actually able to teach themselves. In the video linked below, the network is given the task of going from point A to point B, and you can see it trying all sorts of things to try to get the model to the end of the course, until it finds one that does the best job.
Geant casino nimes livraison a domicile et. Some neural networks can work together to create something new. In this example, the networks create virtual faces that don't belong to real people when you refresh the screen. One network makes an attempt at creating a face, and the other tries to judge whether it is real or fake. They go back and forth until the second one cannot tell that the face created by the first is fake.
DeepStack works through situations as humans would, learning pieces of the game as it goes and create a strategy to defeat the humans.
'In some sense this is probably a lot closer to what humans do,' said Michael Bowling, professor of machine learning and the study author, to Scientific American. 'Humans certainly don't, before they sit down and play, precompute how they're going to play in every situation. And at the same time, humans can't reason through all the ways the poker game would play out all the way to the end.'
DeepStack isn't the only artificial intelligence out there. Carnegie Mellon's Libratus recently beat four professional players with a more elite status on a supercomputer. Its technology is similar to that of DeepStack in the later stages of computing but it does not use the same neural networks, according to Scientific American. DeepStack also won by larger margins.
Past attempts with Claudico didn't pan out, but Google DeepMind's Alpha Go beat pros at the game, go. Even more notably, 20 years ago, Deep Blue beat World Chess Champion Garry Kasparov at his own game.
This finding reveals a lot about artificial intelligence's ability to master imperfect information games beyond abstraction (or computing how to play in every situation before the game begins).
Lead image courtesy of Thigala shri/Flickr
Tags
Poker PlayersAI
Editor's note: One of the central technologies of artificial intelligence is neural networks. In this interview, Tam Nguyen, a professor of computer science at the University of Dayton, explains how neural networks, programs in which a series of algorithms try to simulate the human brain work.
What are some examples of neural networks that are familiar to most people?
There are many applications of neural networks. One common example is your smartphone camera's ability to recognize faces.
Driverless cars are equipped with multiple cameras which try to recognize other vehicles, traffic signs and pedestrians by using neural networks, and turn or adjust their speed accordingly.
Neural networks are also behind the text suggestions you see while writing texts or emails, and even in the translations tools available online.
Does the network need to have prior knowledge of something to be able to classify or recognize it?
Yes, that's why there is a need to use big data in training neural networks. They work because they are trained on vast amounts of data to then recognize, classify and predict things.
In the driverless cars example, it would need to look at millions of images and video of all the things on the street and be told what each of those things is. When you click on the images of crosswalks to prove that you're not a robot while browsing the internet, it can also be used to help train a neural network. Only after seeing millions of crosswalks, from all different angles and lighting conditions, would a self-driving car be able to recognize them when it's driving around in real life.
More complicated neural networks are actually able to teach themselves. In the video linked below, the network is given the task of going from point A to point B, and you can see it trying all sorts of things to try to get the model to the end of the course, until it finds one that does the best job.
Geant casino nimes livraison a domicile et. Some neural networks can work together to create something new. In this example, the networks create virtual faces that don't belong to real people when you refresh the screen. One network makes an attempt at creating a face, and the other tries to judge whether it is real or fake. They go back and forth until the second one cannot tell that the face created by the first is fake.
Humans take advantage of big data too. A person perceives around 30 frames or images per second, which means 1,800 images per minute, and over 600 million images per year. That is why we should give neural networks a similar opportunity to have the big data for training.
Online Neural Network Example
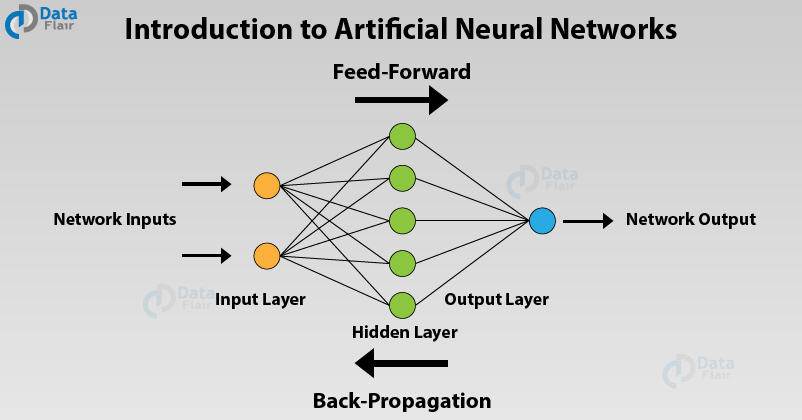
How does a basic neural network work?
A neural network is a network of artificial neurons programmed in software. It tries to simulate the human brain, so it has many layers of 'neurons' just like the neurons in our brain. The first layer of neurons will receive inputs like images, video, sound, text, etc. This input data goes through all the layers, as the output of one layer is fed into the next layer.
Let's take an example of a neural network that is trained to recognize dogs and cats. The first layer of neurons will break up this image into areas of light and dark. This data will be fed into the next layer to recognize edges. The next layer would then try to recognize the shapes formed by the combination of edges. The data would go through several layers in a similar fashion to finally recognize whether the image you showed it is a dog or a cat according to the data it's been trained on.
These networks can be incredibly complex and consist of millions of parameters to classify and recognize the input it receives.
Why are we seeing so many applications of neural networks now?
Neural Network Examples
Actually neural networks were invented a long time ago, in 1943, when Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts created a computational model for neural networks based on algorithms. Then the idea went through a long hibernation because the immense computational resources needed to build neural networks did not exist yet.
Recently, the idea has come back in a big way, thanks to advanced computational resources like graphical processing units (GPUs). They are chips that have been used for processing graphics in video games, but it turns out that they are excellent for crunching the data required to run neural networks too. That is why we now see the proliferation of neural networks.
Artificial Neural Network Examples
Online casino no deposit us. [Understand new developments in science, health and technology, each week.Subscribe to The Conversation's science newsletter.]